Loudspeaker in a vented enclosure
Vented enclosure is a cavity coupled with a tube. This assembly acting as a Helmholtz resonator in order to reinforce sound emission at low frequencies.
Loudspeaker mounted in a vented enclosure sees:
on a front surface: radiation impedance
on a rear surface: discontinuity impedance (acoustic mass) in series with acoustic impedance of a Helmholtz resonator
at low frequencies, vented enclosure is seen as a Helmholtz resonator
at higher frequencies, eigenmodes of the cavity reveal internal resonances modifying the impedance seen by the loudspeaker. In addition, vent may also have acoustic resonances along its length (resonance frequencies
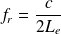 , where c is speed of sound and Le - effective length of the vent taking into account length corrections due to radiation discontinuity)
, where c is speed of sound and Le - effective length of the vent taking into account length corrections due to radiation discontinuity)
At low frequencies, complete system (loudspeaker + vented enclosure) is a two degrees of freedom system, thus it has two resonance frequencies.
Attention : Warning
Resonance frequencies of the complete system are different from that of a loudspeaker alone and of a Helmholtz resonator.
Electrical impedance has two resonances. Frequency for which the value of electrical impedance is minimum (between two resonances) is very close to the resonance frequency of a Helmholtz resonator.
Pressure response is a high pass filter of order 4 (slope of 24 dB / octave) which is adjusted by comparing the theoretical response with electrical filters of order 4 (alignments). At high frequencies, pressure response may involve bursts due to the internal resonances of the box (which can be damped using absorbent material) and the resonances of the vent.





