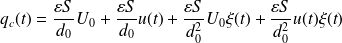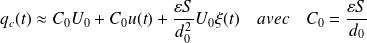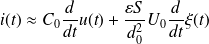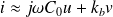Second equation of electrostatic coupling
The voltage
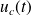 across an electrostatic transducer is the sum of a DC component
across an electrostatic transducer is the sum of a DC component
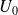 and an AC component u(t) :
and an AC component u(t) :
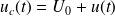 .
.
The electrical charge
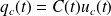 of an electrostatic transducer is therefore written,
of an electrostatic transducer is therefore written,
|
By neglecting the second order terms:
|
By conserving only the AC component of this equation, and observing that the current i is the temporal derivative of the charge Q,
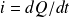 and that the velocity
and that the velocity
 of the membrane is the temporal derivative of the displacement
of the membrane is the temporal derivative of the displacement
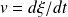 , the temporal derivative of the coupling equation is written
, the temporal derivative of the coupling equation is written
|
In the harmonic domain
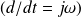 , this equation is written
, this equation is written
|
where
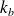 is the electrostatic coupling factor
is the electrostatic coupling factor