Harmonic distortion
A real system will generate harmonics
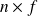 of its input signals frequency
of its input signals frequency
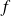 . These harmonics will be added to the original frequency in the output. This is called harmonic distortion.
. These harmonics will be added to the original frequency in the output. This is called harmonic distortion.
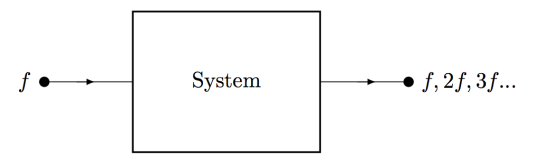
The total harmonic distortion (THD) can be calculated with the following equation :
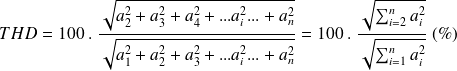 ,
,
where
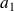 is the RMS value of the fundamental signal, whereas
is the RMS value of the fundamental signal, whereas
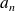 (for
(for
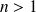 ) are the RMS values of the harmonics.
) are the RMS values of the harmonics.
Microphone manufacturers often include a value for the THD for a given pressure level, for example
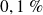 at
at
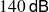 , which corresponds to a satisfactory performance.
, which corresponds to a satisfactory performance.
In the case of loudspeakers, the maximum input power rating is given. This corresponds to the level that the loudspeakers can withstand for at least 8 hours without damage. This rating, however, does not give any indication of the distortion, which can rise to very high levels with the highest input power.
When specifying the THD or THD+N (Total Harmonic Distortion plus Noise), the following information should be specified :
Output power,
Load,
Number of harmonics taken into account,
Input frequency,
System Gain.





